In modern fluid control systems, durability, performance, and reliability are non-negotiable requirements. Among the many types of industrial valves, the ductile iron gate valve stands out as one of the most trusted solutions for waterworks, wastewater treatment, fire protection networks, and industrial pipelines. Its unique combination of strength, flexibility, and corrosion resistance has made it a mainstay in industries where operational safety and long service life are critical.
Ductile iron itself represents a significant advancement in metallurgy. Unlike traditional gray cast iron, which is brittle and prone to cracking, ductile iron is engineered with spheroidal graphite inclusions. These microscopic nodules provide elasticity and toughness, allowing the material to withstand high stress and resist catastrophic failure. This property is particularly valuable in valve construction, where both mechanical strength and resilience against wear are essential.
With operating temperature limits of up to 1350°F (730°C) and pressure ratings in Class 150 and Class 300, ductile iron gate valves offer versatility across a wide range of applications. Class 150 models typically handle 250 psi, while Class 300 versions can manage pressures of up to 640 psi, making them suitable for demanding high-pressure pipelines. Combined with protective epoxy coatings and resilient sealing elements, ductile iron gate valves provide long-term performance even in aggressive environments.
This article explores the fundamental characteristics, components, applications, advantages, and maintenance practices of ductile iron gate valves, offering a comprehensive guide for engineers, procurement specialists, and industry professionals.

A ductile iron gate valve is a type of linear-motion valve designed to start, stop, or regulate the flow of liquids in large-diameter pipelines. The valve operates through a wedge-shaped gate that moves perpendicularly across the fluid stream. When fully raised, the gate allows unobstructed flow with minimal resistance. When fully lowered, it seats tightly against resilient sealing materials—commonly EPDM rubber encapsulation—to prevent leakage.
Key features include:
High strength and corrosion resistance due to ductile iron construction.
Excellent sealing performance, minimizing leakage.
Durable epoxy coatings for enhanced protection against rust.
Pressure capability up to 640 psi depending on class.
Wide application in municipal water systems, fire protection, sewage treatment, and industrial plants.
In simple terms, the ductile iron gate valve is a robust, long-lasting solution that combines mechanical durability with excellent fluid control.
Gate valves play a crucial role in virtually every sector where controlled fluid transmission is required. Their primary function is to stop or allow flow, rather than fine-tuning it. Unlike globe valves or control valves, gate valves are not typically used for throttling because partial openings can cause turbulence, erosion, and damage to the gate.
Instead, gate valves excel in situations where:
Full open or full shutoff is needed.
Minimal flow resistance is required (low pressure drop).
Reliability under high pressure is crucial.
Large-diameter pipelines need shutoff capability.
This makes them indispensable in water distribution networks, power plants, petrochemical industries, and firefighting systems.
The operation of a ductile iron gate valve is straightforward yet highly effective:
Open Position – When the gate is fully lifted, fluid flows freely through the valve with minimal resistance.
Closed Position – Lowering the gate positions it firmly against the valve seat, creating a watertight seal.
Intermediate Position – While possible, operating the valve partially open is not recommended, as it may lead to turbulence and accelerated wear.
This binary nature of operation—either fully open or fully closed—makes gate valves reliable in providing clear and predictable system performance.
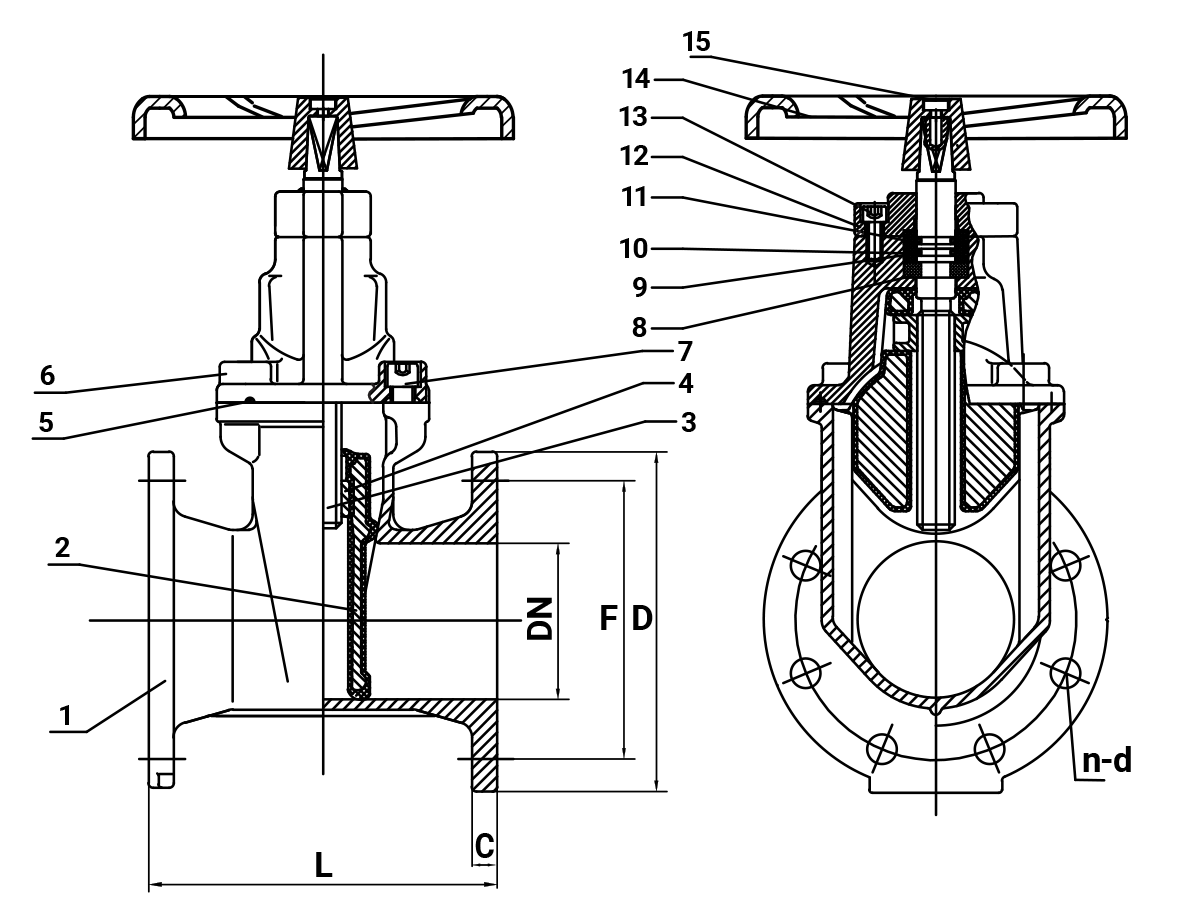
Understanding the anatomy of a gate valve provides insight into its performance and durability.
The housing that contains the internal components.
Made from ductile iron for strength and pressure resistance.
The movable barrier controlling flow.
Often EPDM-coated to ensure tight sealing.
A threaded rod connected to the gate.
Operated manually via handwheel or automatically with actuators.
Covers the valve body and protects internal parts.
Can be bolted or screwed, depending on design.
Contact surface where the gate seals.
Usually made from resilient, corrosion-resistant materials.
Each component is engineered to perform under harsh conditions while maintaining system safety and reliability.
Ductile iron gate valves offer several advantages compared to traditional cast iron or other materials:
High Strength and Ductility – Resistant to cracking under stress.
Corrosion Resistance – Epoxy coatings and encapsulated gates extend service life.
Cost-Effectiveness – More affordable than stainless steel, yet offering similar durability in many applications.
Versatility – Suitable for potable water, wastewater, fire protection, and industrial fluids.
Tight Sealing – Resilient seats ensure leak-free performance.
Minimal Flow Resistance – Straight-through bore minimizes pressure loss.
These benefits explain their widespread adoption across industries.
Ductile iron gate valves are found in numerous critical sectors:
Water Supply Systems – Ensuring reliable shutoff in municipal pipelines.
Wastewater Treatment – Handling corrosive and abrasive media in sewage plants.
Fire Protection – Serving as key shutoff valves in hydrant networks and sprinkler systems.
Industrial Plants – Managing process water, chemicals, and other fluids.
Power Generation – Regulating cooling water systems.
Marine Applications – Used in shipboard piping due to durability and resistance.
Their broad adaptability makes them a trusted choice wherever reliability and long-term performance are needed.
Different configurations exist to suit various needs:
Resilient Seated Gate Valve – Features rubber-encapsulated wedge for improved sealing.
Metal Seated Gate Valve – Used in higher temperature or abrasive conditions.
Rising Stem Gate Valve – Stem moves up/down, offering clear visual position indication.
Non-Rising Stem Gate Valve – Compact design, ideal for underground installations.
Flanged End Gate Valve – Easy connection to flanged pipelines.
Mechanical Joint Gate Valve – Common in waterworks installations.
Each type is tailored to specific environments, pressures, and installation constraints.
To ensure performance and safety, ductile iron gate valves adhere to several international standards, including:
AWWA C509/C515 – American standards for resilient-seated gate valves.
EN 1171 – European standard for cast iron gate valves.
ISO 7259 – International guidelines on valve performance.
API 600/602 – Standards covering gate valve design and testing.
Compliance with these standards guarantees reliability, interchangeability, and safety in critical infrastructure.
To ensure ductile iron gate valves deliver reliable performance throughout their lifespan, industries must adopt structured maintenance programs. Regular attention not only minimizes unexpected failures but also reduces long-term operational costs.
Routine inspections are the first line of defense, allowing operators to detect early signs of leakage, corrosion, or wear before they escalate into major problems. Visual checks of valve bodies, bonnets, and stems help verify structural integrity.
Lubrication is equally important. Applying the correct lubricant to the stem threads reduces friction, ensures smooth operation, and prevents unnecessary strain on the handwheel or actuator.
Seal replacement should be performed proactively. Worn seats, gaskets, or packing can compromise the sealing capability, leading to system inefficiencies or leakage. Timely replacement preserves both safety and performance.
To prevent valves from seizing, it is advisable to exercise valves periodically. Opening and closing them fully keeps the components functional and avoids buildup of deposits inside the valve body.
Lastly, preserving protective coatings is vital. Epoxy layers safeguard ductile iron from rust and environmental degradation, extending service life.
When these best practices are followed consistently, ductile iron gate valves can operate dependably for decades, making them a cost-effective choice for critical infrastructure.
While ductile iron gate valves offer many advantages, users should be aware of certain limitations:
Weight – Heavier than plastic or composite alternatives.
Temperature Restrictions – Though strong, ductile iron has lower thermal limits compared to stainless steel.
Corrosion Potential – If epoxy coatings fail, rusting can occur.
Not Ideal for Throttling – Gate valves are designed for on/off service, not precise flow control.
Understanding these limitations helps engineers select the right valve for specific conditions.
With global demand for reliable water infrastructure and sustainable industrial systems rising, ductile iron gate valves are expected to remain essential. Future advancements may include:
Improved Coating Technologies – Enhancing corrosion resistance.
Smart Monitoring Sensors – Allowing predictive maintenance.
Lightweight Alloys and Hybrids – Reducing weight while maintaining strength.
Green Manufacturing – Utilizing more environmentally friendly production methods.
Such innovations will further extend the reliability and efficiency of ductile iron gate valves in the decades ahead.
The ductile iron gate valve represents a balance of durability, affordability, and performance. By combining the mechanical strength of ductile iron with resilient sealing technology, these valves ensure reliable service across a wide spectrum of industries. From municipal water supply to fire protection and industrial processing, they continue to serve as indispensable components in modern infrastructure.
As industries face growing demands for efficiency, safety, and sustainability, ductile iron gate valves will remain a cornerstone of pipeline systems worldwide. For engineers, operators, and decision-makers, understanding their design, advantages, applications, and limitations is key to making informed choices that deliver long-term value.