Globe valves play a critical role in controlling fluid flow within industrial systems. Renowned for their robust construction and precise flow regulation, these valves are essential components in HVAC systems, steam systems, hot water heating systems, and chiller applications. The design of a globe valve consists of a linear travel plug that moves within a spherical body, modulating flow by varying the plug's proximity to the seat. When the plug is fully lowered, it seals the flow entirely, providing tight shutoff capabilities.
Due to their wide range of applications and their ability to offer accurate throttling, globe valves are commonly found in industrial plants and HVAC systems that require precise control of flow rates. However, to maintain their efficiency and longevity, regular maintenance is crucial. Proper upkeep helps minimize unexpected breakdowns, reduces operational costs, and prolongs valve life. This article delves into the essential aspects of globe valve maintenance, from inspection to alignment, providing a comprehensive guide to keeping your globe valves in optimal condition.
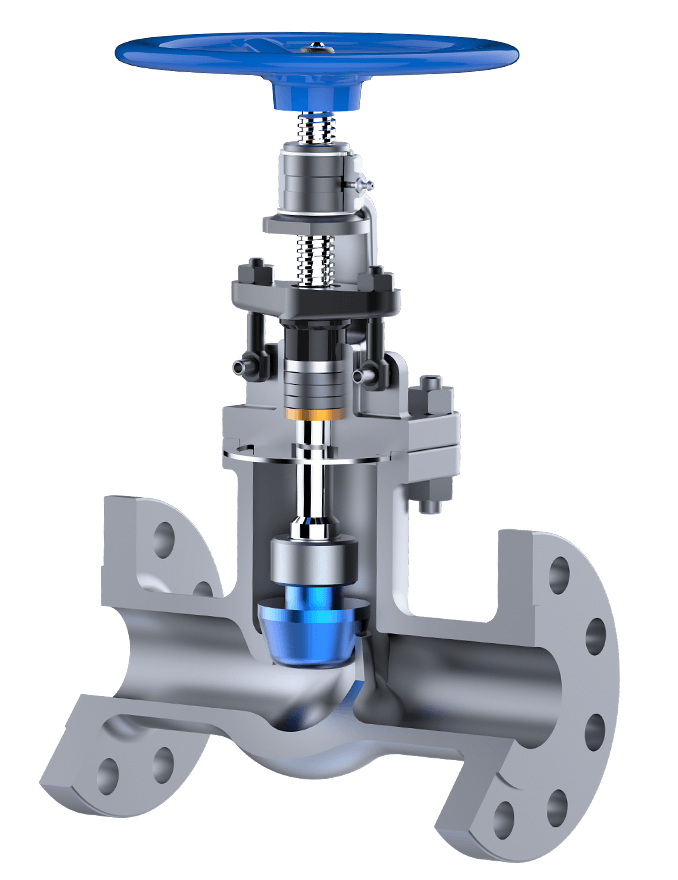
Proper globe valve maintenance ensures not only the longevity of the valve but also the safety and efficiency of the entire system. Due to their role in controlling flow in critical applications, any failure or leakage can result in costly downtime and potential safety hazards. Regular maintenance reduces the risk of operational failures and enhances valve performance, thereby minimizing energy consumption and maintenance costs.
Effective globe valve maintenance also contributes to maintaining system integrity. For instance, in HVAC systems where temperature regulation is vital, a malfunctioning valve can lead to temperature fluctuations, compromising comfort and efficiency. Regular maintenance practices help preserve the valve’s integrity, ensuring smooth and precise operation over time.
The maintenance routine for a globe valve should follow a systematic approach that includes inspection, cleaning, lubrication, and necessary adjustments. Here’s a breakdown of each step:
Routine inspection is the first step toward identifying potential problems before they escalate. During inspections, it’s essential to assess the following components:
Packing, Disc, and Seat: Examine these areas for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. Packing is particularly prone to degradation, leading to leakage.
Valve Body and Bonnet: Inspect for signs of erosion or cavitation, especially if the valve is used in aggressive or high-pressure environments.
Leak Detection: Look for fluid leaks around the bonnet, stem, and flange connections. Leaks can indicate packing failure or damage to internal components.
Stem and Yoke Inspection: Check the stem for corrosion or bending. The yoke should be intact and free from obstructions.
Disk Alignment: Ensure the valve disk aligns correctly with the flow direction. Misalignment can hinder flow control and cause premature wear.
Keep detailed records of inspection dates and findings to track valve condition over time.
Use specialized tools to measure wear and deformation, ensuring accurate assessments.
One of the most crucial aspects of globe valve maintenance is cleaning and lubricating moving parts. Accumulated debris can hinder performance and lead to premature wear.
Disassemble the Valve: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to safely disassemble the valve without causing damage.
Remove Debris: Use a clean, lint-free cloth or a soft brush to remove dirt, rust, or foreign particles.
Clean Valve Seats: Use a non-abrasive cleaner to wipe down valve seats, ensuring smooth and clean surfaces for sealing.
Flush with Appropriate Solvent: In some cases, a suitable solvent may be required to dissolve residues and buildup.
Select the Appropriate Lubricant: Use lubricants recommended by the valve manufacturer, especially those compatible with the medium being controlled.
Apply to Moving Parts: Focus on the stem, packing, and yoke. Lubrication reduces friction and prevents binding.
Reassemble and Test: Once reassembled, cycle the valve to ensure smooth operation.
Over time, globe valve seats and discs may develop irregularities due to wear or corrosion, resulting in leaks or poor sealing performance. Lapping and reseating help restore a smooth, even surface, enhancing the valve’s ability to shut off properly.
Disassemble the Valve: Remove the disk and seat components.
Apply Lapping Compound: Use a fine-grit lapping compound to coat the seat surface.
Lapping Motion: Move the disk against the seat in a figure-eight pattern, applying light pressure.
Clean and Inspect: After lapping, thoroughly clean the components and inspect for smoothness.
Reassemble and Test: Verify that the valve seals properly before placing it back into operation.
Reseating involves reshaping the valve seat to eliminate imperfections. It is typically performed if lapping alone does not achieve a proper seal.
Packing adjustment is vital to maintaining a tight seal without introducing excessive friction on the valve stem. Globe valves commonly use graphite or PTFE packing materials, which can wear out over time.
Identify Leakage: Detect leaks around the stem or bonnet.
Tighten the Gland Bolts: Use the correct torque to tighten the bolts gradually and evenly.
Check Stem Movement: After adjustment, the stem should move smoothly without resistance.
Monitor Post-Adjustment: Observe for continued leakage or increased friction.
When tightening does not resolve leakage, it may be necessary to replace the packing. Always use manufacturer-recommended packing material to ensure compatibility and performance.
The bonnet gland assembly is crucial for maintaining a pressure-tight seal. Regular maintenance involves checking gland bolts and replacing gaskets or packing as necessary.
Inspect the Gland Bolts: Tighten or replace any loose or damaged bolts.
Gasket Inspection: Replace worn gaskets to prevent leaks.
Reassembly: Properly torque the bolts to maintain an effective seal.
Maintaining proper valve orientation and disk alignment is crucial for optimal flow control. During maintenance, it’s essential to verify that the disk correctly aligns with the flow path. Improper alignment can reduce efficiency and cause wear on internal components.
Disassemble the Valve: Remove the valve disk for inspection.
Check Alignment Marks: Verify that the disk orientation matches the flow direction indicated by the manufacturer.
Correct Misalignment: Adjust the disk as needed to restore proper orientation.
Final Inspection: Once reassembled, test the valve to ensure smooth operation and adequate sealing.
During maintenance, operators may encounter several common issues, including:
Sticking Stems: Caused by inadequate lubrication or corrosion. Clean and lubricate the stem to restore function.
Seat Leakage: May result from worn seats or improper lapping. Perform lapping or reseating as necessary.
Excessive Vibration: Often linked to loose components or improper alignment. Tighten connections and ensure proper disk alignment.
Corrosion and Erosion: Regular inspections can help detect early signs of corrosion, allowing timely maintenance.
Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Always adhere to the manufacturer’s maintenance instructions and use approved materials.
Record Keeping: Maintain detailed logs of maintenance activities, including inspection dates, performed tasks, and outcomes.
Train Personnel: Ensure that maintenance personnel are trained in the correct procedures and safety protocols.
Schedule Maintenance: Regular maintenance intervals help prevent sudden breakdowns and reduce downtime.
Globe valve maintenance is an integral part of ensuring system efficiency and reliability. By conducting thorough inspections, regular cleaning, proper lubrication, and precise adjustments, operators can significantly extend valve life and maintain optimal performance. Whether in HVAC systems or industrial applications, adopting a proactive maintenance strategy is essential to minimizing downtime and maintaining fluid control integrity.
Incorporating these best practices into your maintenance routine will ensure your globe valves remain functional and efficient, safeguarding your systems from unexpected failures and costly disruptions.