In today's energy-intensive and safety-critical industries, valve performance is no longer measured only by basic flow control. Modern facilities demand equipment that can withstand extreme pressure, high temperatures, aggressive media, and long service cycles—while maintaining tight shutoff, stable regulation, and operational safety. Among the most trusted solutions in such environments is the API 600 pressure seal globe valve, a specialized valve design developed to meet the rigorous requirements of power generation, oil and gas, petrochemical, and refinery applications.
As industries worldwide expand thermal power plants, upgrade upstream and downstream oil and gas infrastructure, and adopt more demanding operating conditions, pressure seal globe valves have become a cornerstone of high-integrity flow control. This article explores what makes API 600 pressure seal globe valves unique, how they differ from conventional bolted bonnet designs, where they are used, and why they continue to be the preferred choice for critical services.
API 600, issued by the American Petroleum Institute, is a globally recognized standard that defines design, materials, testing, and performance requirements for steel gate valves used in refinery, petrochemical, and related industrial services. While API 600 is most commonly associated with gate valves, its design philosophy—robust construction, strict material specifications, and high-pressure capability—also influences the engineering of pressure seal globe valves used in similar environments.
Pressure seal globe valves built in accordance with API 600 principles are engineered for:
- High-pressure ratings (typically Class 600, 900, 1500, and above)
- High-temperature service (often exceeding 450°C in power plants)
- Zero or minimal leakage requirements
- Long-term reliability under thermal cycling
These valves are not designed for light-duty control but for severe, mission-critical operations where failure is not an option.
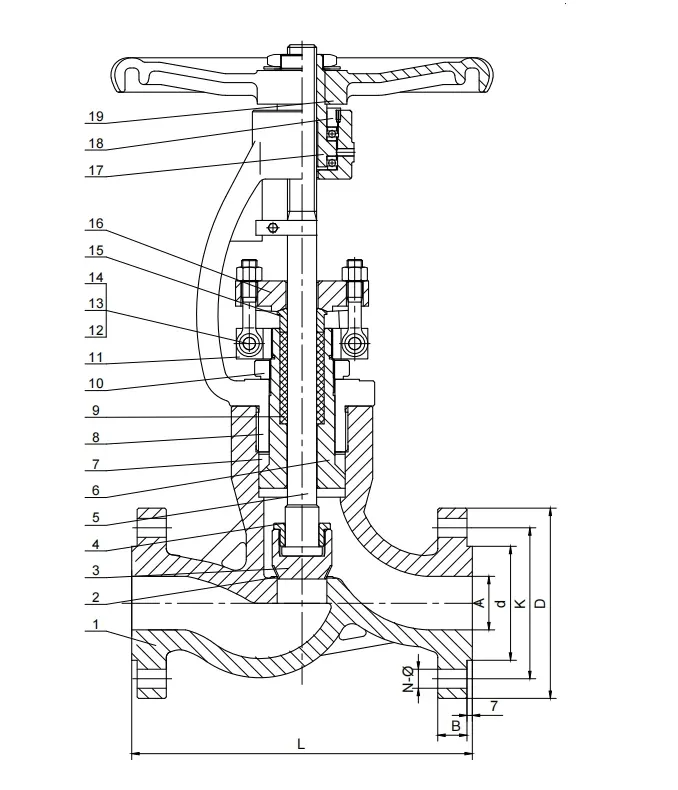
A globe valve is a linear-motion valve designed primarily for throttling and regulating flow. It consists of a movable disk (plug) and a stationary ring seat, allowing precise control over flow rate, pressure, and temperature. Unlike gate valves, which are primarily isolation devices, globe valves are optimized for control applications.
A pressure seal globe valve is distinguished by its bonnet design. Instead of using traditional bolted flanges and gaskets to seal the bonnet-to-body joint, a pressure seal valve employs a self-energizing sealing mechanism. As internal pressure increases, it enhances the sealing force at the bonnet joint, reducing the risk of leakage and gasket blowout.
This design is particularly valuable in:
- High-pressure steam lines
- Superheated steam and feedwater systems
- High-temperature hydrocarbon services
- Boiler and turbine auxiliary systems
The defining feature of a pressure seal globe valve is its pressure-activated bonnet joint. In conventional bolted bonnet valves, sealing depends primarily on gasket compression achieved by tightening bolts. Over time, thermal cycling, vibration, and material relaxation can reduce gasket effectiveness, increasing the risk of leaks.
In contrast, the pressure seal design uses a metal-to-metal seating arrangement combined with a soft sealing element (often graphite or a metal-reinforced gasket). When internal pressure rises, it pushes the bonnet upward against the sealing surface, increasing the contact stress and tightening the seal automatically.
Key Advantages of Pressure Seal Construction:
- Leak-tight performance under high pressure
- Reduced risk of gasket blowout
- Better performance under thermal expansion and contraction
- Lower maintenance frequency compared to bolted bonnets
This self-energizing feature makes pressure seal globe valves especially suitable for applications where pressure and temperature fluctuate widely.
API 600 pressure seal globe valves are built from high-grade materials selected to withstand extreme operating conditions. Common body and bonnet materials include:
- Carbon steel (ASTM A216 WCB, A105) for general high-pressure service
- Chrome-moly steels (ASTM A217 WC6, WC9, C12) for high-temperature applications
- Stainless steels (CF8, CF8M, F304, F316) for corrosion resistance
- Alloy steels and duplex stainless steels for aggressive chemical or offshore environments
Trim components (plug, seat, stem) are typically manufactured from hardened stainless steel, cobalt-based alloys, or other wear-resistant materials to ensure long service life and tight shutoff even after repeated cycles.
In power plant applications, for example, chrome-moly steels are widely used due to their excellent resistance to creep, oxidation, and thermal fatigue at elevated temperatures.
Pressure seal globe valves are designed to operate reliably at Class 600, 900, 1500, and even Class 2500 pressure ratings. In steam systems, they routinely handle temperatures exceeding 450–550°C without loss of structural integrity.
The globe valve's linear motion and contoured plug design enable precise modulation of flow. When combined with hardened seating surfaces, this ensures:
Accurate throttling
Minimal seat leakage
Stable performance across varying loads
By eliminating gasket blowout risks and improving bonnet joint integrity, pressure seal valves enhance safety in high-energy pipelines, reducing the likelihood of hazardous leaks that could endanger personnel and equipment.
Robust construction, premium materials, and optimized sealing reduce wear and extend maintenance intervals, lowering total cost of ownership.
Pressure seal globe valves are widely used in:
- Main steam lines
- Reheat and superheated steam systems
- Boiler feedwater circuits
- Turbine bypass and auxiliary systems
Their ability to withstand extreme temperature and pressure while providing precise flow control makes them indispensable in coal-fired, gas-fired, nuclear, and combined-cycle power plants.
In upstream, midstream, and downstream operations, these valves are used in:
- High-pressure separation units
- Process heaters and furnaces
- High-temperature hydrocarbon services
- Critical isolation and control points in refineries
Their robust sealing performance is essential for handling volatile and hazardous fluids safely.
In chemical plants, pressure seal globe valves regulate high-temperature reaction flows, heat transfer fluids, and aggressive chemicals, where both tight shutoff and resistance to corrosion are required.
On offshore platforms and marine vessels, pressure seal globe valves provide reliable performance in compact, high-pressure systems exposed to vibration, temperature variation, and corrosive environments.
One of the most common questions among engineers is whether a pressure seal design is necessary for a given application. While bolted bonnet globe valves remain suitable for many moderate-pressure services, the pressure seal design offers distinct advantages in severe conditions.
|
Feature |
Pressure Seal Globe Valve |
Bolted Bonnet Globe Valve |
|
Pressure Capability |
Excellent for high-pressure classes |
Limited at very high pressure |
|
Temperature Resistance |
Superior for high-temperature service |
Adequate for moderate temperatures |
|
Bonnet Sealing |
Self-energizing, pressure-assisted |
Dependent on gasket compression |
|
Maintenance |
Less frequent |
May require periodic re-tightening |
|
Safety |
Lower risk of leakage or blowout |
Higher risk under extreme conditions |
For applications involving high-energy fluids, steam, or thermal cycling, pressure seal globe valves are often the safer and more economical long-term solution.
API 600 pressure seal globe valves undergo stringent quality control and testing to ensure compliance with international standards. Typical tests include:
- Hydrostatic pressure testing of body and seat
- Seat leakage tests to verify tight shutoff
- Material certification and traceability
- Non-destructive testing (NDT) such as radiography or ultrasonic inspection
- Operational and functional testing
Many manufacturers also offer compliance with additional standards such as:
- API 598 (Valve Inspection and Testing)
- ASME B16.34 (Valves—Flanged, Threaded, and Welding End)
- ISO 15848 (Fugitive emissions)
These certifications provide confidence that the valve will perform reliably in critical service.
While globe valves are traditionally associated with manual operation, modern API 600 pressure seal globe valves are increasingly integrated with automation systems. They can be equipped with:
Electric actuators for remote operation
Pneumatic actuators for fast response in control loops
Smart positioners and digital controllers for precise modulation
This allows seamless integration into distributed control systems (DCS) and plant automation architectures, supporting predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and optimized process performance.
The global demand for high-performance control valves continues to grow, driven by:
- Expansion of thermal power generation in developing economies
- Upgrading and retrofitting of aging refinery infrastructure
- Increasing safety and environmental regulations
- Growth in LNG, hydrogen, and high-pressure process technologies
Pressure seal globe valves, in particular, are gaining traction as operators seek solutions that reduce leakage, improve safety, and minimize lifecycle costs. Manufacturers are responding with innovations in materials, sealing technologies, and actuator integration.
In regions such as Asia-Pacific, the Middle East, and North America, large-scale investments in power plants, petrochemical complexes, and pipeline networks are accelerating the adoption of API-compliant pressure seal valves.
Choosing the right API 600 pressure seal globe valve requires careful evaluation of operating conditions and system requirements:
Ensure the valve class and materials are suitable for maximum operating pressure and temperature.
Consider corrosion, erosion, and chemical compatibility when selecting body and trim materials.
Determine whether the valve will be used for throttling, on–off service, or both.
Select flanged, butt-weld, or other connection types based on piping design and installation requirements.
Evaluate whether manual, electric, or pneumatic operation is required for the application.
Factor in expected service life, availability of spare parts, and ease of maintenance.
By aligning valve specifications with operational needs, plant operators can achieve optimal performance and long-term reliability.
As industries move toward more sustainable and environmentally responsible operations, valve design plays a critical role in reducing emissions and improving safety. Pressure seal globe valves contribute to these goals by:
- Minimizing fugitive emissions through superior sealing
- Enhancing operational safety in high-energy systems
- Reducing maintenance-related downtime and resource consumption
In power generation, for instance, reliable valve performance supports stable plant operation, improving efficiency and reducing fuel waste. In chemical processing, leak prevention protects both the environment and personnel.
Looking ahead, manufacturers are investing in advanced materials, digital monitoring, and smart diagnostics to further enhance valve performance. Emerging trends include:
- High-performance alloys and coatings for extreme corrosion and temperature resistance
- Integrated sensors for real-time monitoring of pressure, temperature, and valve position
- Predictive maintenance tools using data analytics and AI
- Standardization and modular designs to reduce lead times and simplify installation
These innovations are expected to make pressure seal globe valves even more reliable, efficient, and adaptable to evolving industrial requirements.
API 600 pressure seal globe valves represent the pinnacle of valve engineering for high-pressure, high-temperature, and safety-critical applications. By combining robust construction, advanced sealing technology, and precise flow control, they deliver unmatched performance in power generation, oil and gas, petrochemical, and other demanding industries.
As global infrastructure continues to modernize and operating conditions grow more challenging, the role of pressure seal globe valves will only become more significant. For engineers, plant operators, and procurement professionals seeking long-term reliability, safety, and efficiency, these valves remain an essential component of modern industrial systems.